Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Living in an environmentally sustainable way necessitates
a. | using Earth’s resources efficiently whenever convenient. | b. | living without basic
ecosystem services. | c. | living in a tent. | d. | living in a rural
area. | e. | sensitivity to the needs of future generations. |
|
|
|
2.
|
Five square miles is equal to _____ acres. (1 square mile = 640 acres)
a. | 0.32 | b. | 320 | c. | 2500 | d. | 3200 | e. | 32,000 |
|
|
|
3.
|
The concept of ecological footprint is measured in terms of the amount of
a. | resource an individual consumes daily. | b. | land area. | c. | resources an
individual consumes over the course of a lifetime. | d. | resources an entire nation consumes
yearly. | e. | resources an individual consumes yearly. |
|
|
|
4.
|
An element is a substance that
a. | can be broken down into simpler components. | b. | is made of many
types of atoms. | c. | is made up of molecules. | d. | consists of one type of
atom. | e. | makes up energy. |
|
|
|
5.
|
On the pH scale, _____ is neutral.
|
|
|
6.
|
According to the law of conservation of matter,
I.matter can be
created
II.matter cannot be destroyed
III.after a chemical reaction, the original atoms
remain
a. | I only. | b. | II only. | c. | III
only. | d. | I and II. | e. | II and III. |
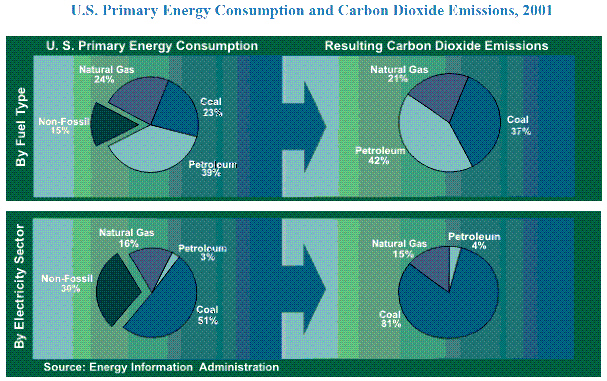
|
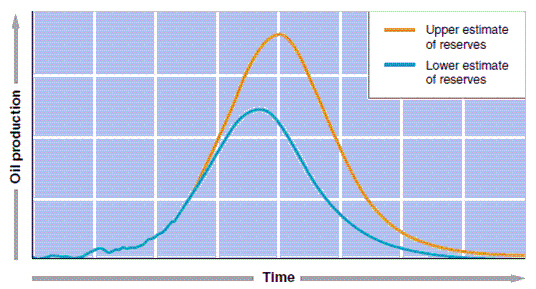
|
|
7.
|
The “ability to do work “ is called
a. | power | b. | joules | c. | energy. | d. | heat | e. | radiation. |
|
|
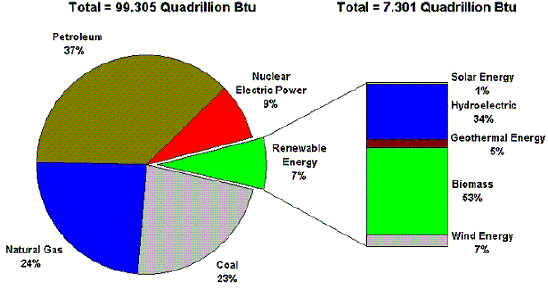
|
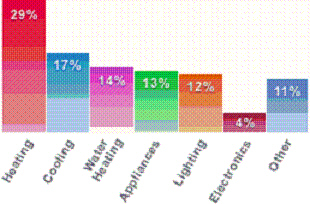
8.
|
In the electrical lines that transmit electricity between a power plant and a
home, _____ percent of the energy is lost as heat and sound.
|
|
|
9.
|
A negative feedback loop is
a. | when feed back into the system increases the rate of progress. | b. | seen in the example
of increased greenhouse gases leading to global warming. | c. | seen in the example
of world population growth. | d. | when a system responds to a change by returning
it to its original state. | e. | Both b and d. |
|
|
|
10.
|
Choose the correct sequence for energy flow within an ecosystem
a. | Herbivores ®
producers ®
carnivores ®
scavengers | b. | Producers ® herbivores ® carnivores ® scavengers | c. | Producers ® carnivores ® herbivores ® carnivores | d. | Scavengers ® producers ® herbivores ® carnivores | e. | Carnivores ® scavengers ® producers ®
herbivores |
|
|
|
11.
|
Which of the following are needed for photosynthesis?
a. | Water, solar energy and carbon dioxide | b. | Water, solar energy and
glucose | c. | Carbon dioxide, energy and glucose | d. | Oxygen, water and energy | e. | Oxygen and
glucose |
|
|
|
Figure 3-1
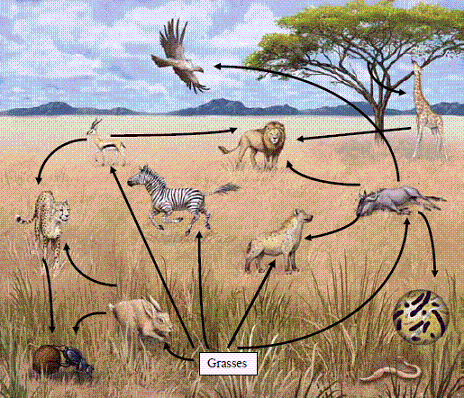
|
|
|
12.
|
Use Figure 3-1. Which of the organisms illustrated above would be considered a
decomposer?
a. | Vulture | b. | Zebra | c. | Hyena | d. | Bacteria | e. | Hare |
|
|
|
13.
|
What impact does deforestation have on the carbon cycle?
a. | Increase in amount of CO2 in the atmosphere | b. | Decrease in the
amount of CO2 in the atmosphere | c. | Increase in the amount of
photosynthesis | d. | Increase in the amount of cellular respiration performed by
autotrophs | e. | Deforestation has no impact on the carbon cycle |
|
|
|
14.
|
When nutrients are transported through soil with water, this process is known
as
a. | Infiltration | b. | Percolation | c. | Decomposition | d. | Leaching | e. | Nitrification |
|
|
|
15.
|
Which of the following is not a part of the carbon cycle?
a. | Transpiration | b. | Combustion | c. | Photosynthesis | d. | Extraction | e. | Respiration |
|
|
|
Figure 4-2
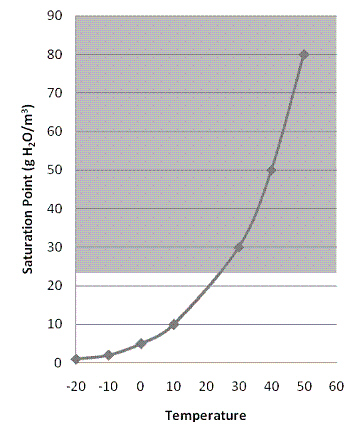
|
|
|
16.
|
Use Figure 4-2. Using the graph above, what conclusion can be drawn about the
relationship between temperature and saturation point?
a. | As temperature increases, saturation point decreases
exponentially | b. | As temperature increases, saturation point increases
exponentially | c. | As temperature increases, saturation point increases linearly | d. | As temperature
increases, saturation point decreases linearly | e. | There is a negative correlation between
temperature and saturation point |
|
|
|
Figure 4-6
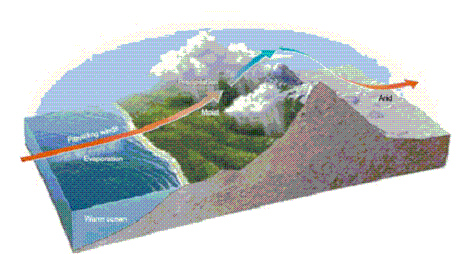
|
|
|
17.
|
Use Figure 4-6. What phenomenon does the above figure represent?
a. | Mountain rain effect | b. | Prevailing ocean winds | c. | Desert
formation | d. | Climate change | e. | Rain shadow
effect |
|
|
|
18.
|
Which of the following are examples of wetlands?
I. Swamps
II.
Marshes
III. Bogs
a. | I only | b. | II only | c. | III
only | d. | I and II | e. | I, II, and III |
|
|
|
19.
|
Which biome has plants with adaptations that prevent water loss, such as smaller
leaves with few pores for gas exchange?
a. | Temperate rain forest | b. | Woodland/shrubland | c. | Temperate seasonal
forest | d. | Tropical rainforest | e. | Subtropical
desert |
|
|
|
Figure 5-3
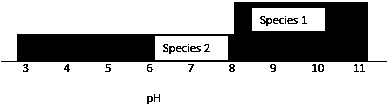
|
|
|
20.
|
Use Figure 5-3. Using the data provided, what is the pH range for the
fundamental niche for species 2?
a. | 1-14 | b. | 3-11 | c. | 5-9 | d. | 7 | e. | 8-11 |
|
|
|
21.
|
The intrinsic growth rate of a population
a. | directly affects environmental resistance. | b. | causes changes in
birth rates without affecting death rates. | c. | causes changes in death rates without affecting
birth rates. | d. | is the maximum rate at which a population may increase. | e. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
22.
|
Many plants have their roots infected with a specialized fungus. The plant
supplies carbon to the fungus, and the fungus supplies nutrients to the plant. This is an
example of a _____ association.
a. | mutualistic | b. | commensalistic | c. | parasitic | d. | successional | e. | predator/prey |
|
|
|
23.
|
The total fertility rate (TFR) is an estimate of
a. | the number of children that will survive to adulthood. | b. | the number of years
a typical infant will live. | c. | the number of children each woman in a
population will have. | d. | the number of births per 1000 people per
year. | e. | the percentage of women in a population that are able to have
children. |
|
|
|
24.
|
Developing countries tend to have a(n) ____ age structure diagram.
a. | rectangular-shaped | b. | inverted triangle | c. | pyramid-shaped | d. | square | e. | round |
|
|
|
25.
|
Populations whose age structure diagrams are narrower at the bottom than at the
top have
a. | high death rates | b. | the same proportion of individuals in each age
group | c. | a declining population | d. | a high growth rate | e. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
26.
|
Many sub-Saharan tribesmen of Africa regularly use the blood, milk, and fur of
their livestock, without killing them. Based on this information alone we might classify this
relationship as ____. However, the cattle actually derive an overall benefit because the herdsman
also protect them from predators and help them find water and food. Therefore, this relationship
should instead be classified as ____.
a. | commensalism; mutualism | b. | mutualism; competition | c. | parasitism;
commensalism | d. | parasitism; mutualism | e. | predation;
parasitism |
|
|
|
27.
|
Using the rule of 70, a population growing at 10% would double in
a. | 7 years | b. | 10 years | c. | 15
years | d. | 17 years | e. | Not enough information to
tell |
|
|
|
Figure 7-1
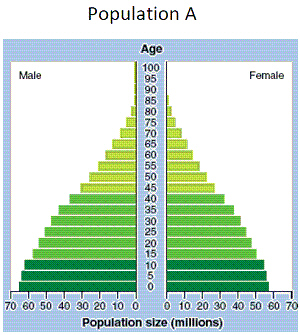 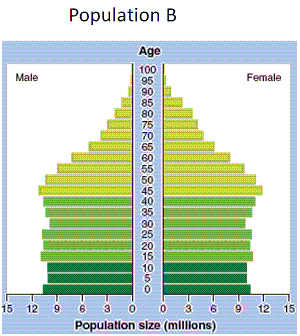
|
|
|
28.
|
Use Figure 7-1. Population A is most likely
a. | rapidly growing. | b. | rapidly declining. | c. | stable or close to
stable. | d. | going to decline in a few decades. | e. | There is not enough information to
tell. |
|
|
|
29.
|
Use Figure 7-1. In pyramid A, what is the approximate number of people in the
bottom 3 cohorts (0-10)?
a. | 200,000,000 | b. | 250,000,000 | c. | 350,000,000 | d. | 450,000,000 | e. | 500,000,000 |
|
|
|
30.
|
Use Figure 7-1. Population A would most likely be in which stage of demographic
transition?
|
|
|
31.
|
Which of the following chemical reactions are involved in the creation of acid
rain?
I. sulfur dioxide and water vapor combine to create sulfuric acid
II. hydrogen and
chlorine combine to create hydrochloric acid
III. sulfur and oxygen combine to create sulfur
dioxide
a. | I only | b. | II only | c. | III
only | d. | I and II | e. | I and III |
|
|
|
32.
|
Topsoil is often considered to be found in what two horizons.
a. | O and A horizon. | b. | O and B horizon. | c. | A and B
horizon. | d. | A and C horizon. | e. | parent
material. |
|
|
|
33.
|
The least weathered zone in a soil is the
a. | A horizon. | b. | O horizon. | c. | E
horizon. | d. | C horizon. | e. | B horizon. |
|
|
|
34.
|
The water table is
a. | anywhere water is visible on the surface. | b. | where streams and
lakes intersect. | c. | the uppermost level at which water fully saturates rock or soil. | d. | synonymous with
groundwater. | e. | where water under pressure rises. |
|
|
|
35.
|
Eutrophic lakes
a. | have very low productivity as a result of acid rain. | b. | have very high
productivity as a result of high levels of nutrients. | c. | have low nutrient levels. | d. | are formed by
glaciers. | e. | usually have absolutely no fish. |
|
|
|
36.
|
The effect(s) of dams include
a. | impediment to fish migration. | b. | displacement of people. | c. | reduction of fossil
fuel use. | d. | reduction of seasonal flooding. | e. | all of these answers are
correct. |
|
|
|
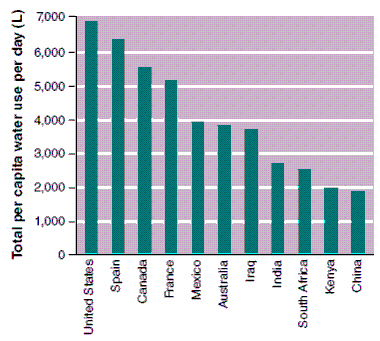
Figure 9-3
|
|
|
37.
|
Use Figure 9-3. According to the figure above, what is the approximate total
water usage for South Africa, Mexico, and France?
a. | 6,000 L/per day | b. | 11,700 L/per day | c. | 13,000 L/per
day | d. | 15,000 L/per day | e. | 23,500 L/per
day |
|
|
|
38.
|
You are selecting a new dishwasher. You do about 150 loads per year. The less
efficient model uses 9 gallons per load. The more efficient model uses 6 gallons per load. How much
money will be saved on water if you select the more efficient model and the price of water is $0.75
per 1000 gallons?
a. | $0.34 | b. | $3.30 | c. | $33 | d. | $330 | e. | $3000 |
|
|
|
39.
|
Gray water is suitable for
a. | drinking. | b. | washing clothing. | c. | washing
cars. | d. | watering plants. | e. | both c and d. |
|
|
|
40.
|
One example of the tragedy of the commons can occur when several farmers share
the same pasture for feeding sheep. The root cause of this tragedy is that
a. | people are bad | b. | sheep reproduce too quickly | c. | the market cannot
support too many farmers | d. | the farmers believe that if I don’t use
it then someone else will. | e. | the cost of the sheep is lessened by bulk
purchase power |
|
|
|
41.
|
When looking at both private and public lands in the US the most common use
is
a. | Timber Production | b. | Grazing Land | c. | Recreational | d. | Defense | e. | Residential |
|
|
|
42.
|
The major complaint that environmental detractors of the Taylor Grazing Act have
is that
a. | The negative externalities of grazing are not fully revealed | b. | The taxes in grazing
animals are too high | c. | The fences erected as a result of this
legislation are deleterious for wildlife | d. | It allows too much grazing to take
place | e. | There are no environmental detractors to the Taylor Grazing
Act |
|
|
|
43.
|
Which of the following is NOT a result of urban sprawl?
a. | The average number of miles driven in the US annually has tripled over the past 50
years | b. | Due to larger parcel size suburban populations use twice as much land area as
similarly sized urban populations | c. | Distance between work, goods, services, and
home prevents pedestrian travel | d. | Lower population densities make services such
as mass transit economically prohibitive | e. | Air pollution increases due to reliance on
personal vehicles for transportation |
|
|
|
44.
|
Eminent Domain is a tool that can be used to assist in smart growth. This tool
allows
a. | Citizens to sue the government if they feel that they are being
ignored | b. | Citizens to sue the government if they feel that government practices are leading
directly to urban blight | c. | Governments to force land use restrictions on
citizens to prevent urban blight | d. | Governments to force land use restrictions on
citizens to prevent any environmental problems (per the National Environmental Protection Act,
NEPA) | e. | Governments to acquire land at fair market value even if the owner does not wish to
sell it |
|
|
|
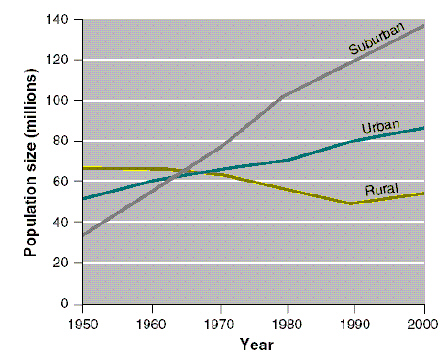
Figure 10-1
|
|
|
45.
|
Use Figure 10-1. What was the approximate US population in 2000?
a. | 150 million | b. | 180 million | c. | 230
million | d. | 280 million | e. | 330 million |
|
|
|
46.
|
Use Figure 10-1. Urban populations increased approximately ____ % from 1950 to
2000.
|
|
|
Figure 10-2
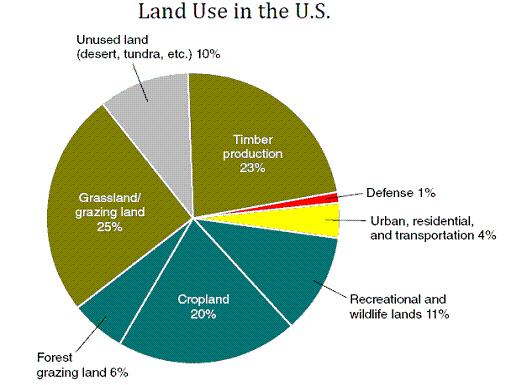
|
|
|
47.
|
Use Figure 10-2. What of the following land use areas would most likely have the
least amount of fragmentation?
a. | Urban, residential and transportation | b. | Desert and Tundra | c. | Defense | d. | Timber production | e. | Croplands |
|
|
|
48.
|
After many years of applying the selective pesticide provironex, a farmer
notices that the applications seem less effective. This is likely due to
a. | The fact that provironex is fat soluble and has been
bioaccumulating | b. | Provironex is selective, so other pests are filling the niche from the exterminated
ones | c. | Provironex is persistent, and the farmer should apply less for better
results | d. | The target species has begun to evolve resistance | e. | Provironex is a wide
spectrum pesticide that needs to be fine tuned for the target species |
|
|
|
49.
|
Scientists have inserted a gene for the production of vitamin A into rice. This
practice of changing the genetic structure of agricultural products to improve desirable traits is
known as
a. | Genetic Engineering | b. | Transmodification | c. | Selective
Breeding | d. | Natural Selection | e. | Animal
Husbandry |
|
|
|
50.
|
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is likely to use all of the following
techniques EXCEPT
a. | Crop rotation | b. | Intercropping | c. | Planting herbicide
resistant crops | d. | Habitat creation for pest predators | e. | Increased use of traditional
pesticides |
|
|
|
51.
|
Worldwide, the largest component of the human diet is
a. | Grain products | b. | Meat products | c. | Dairy
products | d. | Raw and processed sugars | e. | Fruits and
vegetables |
|
|
|
52.
|
Currently the world’s farmers grow enough grain to feed
a. | About a quarter of the world’s population | b. | About a third of the
world’s population | c. | About half of the world’s
population | d. | About 75% of the world’s population | e. | More than the
world’s population |
|
|
|
Figure 11-1
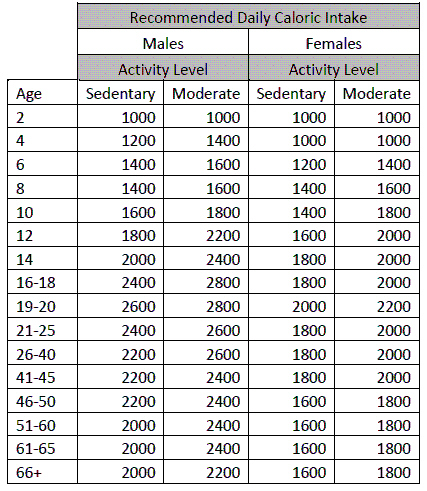
|
|
|
53.
|
Use Figure 11-1. Based on the above recommended daily allowances, which of the
following categorical groups would require the largest caloric intake?
a. | Adolescent males | b. | Adolescent females | c. | Infant
males | d. | Infant females | e. | Young men |
|
|
|
Figure 11-2
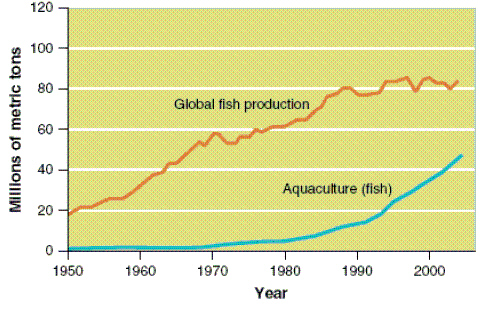
|
|
|
54.
|
Use Figure 11-2. Between which years did Aquaculture fish production increase
the most?
a. | 1950 and 1960 | b. | 1960 and 1970 | c. | 1970 and
1980 | d. | 1990 and 2000 | e. | It has not increased in the last 50
years |
|
|
|
The following chart displays world marketed energy consumption based on a
reference case developed by the US Energy Information Administration in which the energy consumption
increases by 49% from 2007 to 2035. Figure 12-1
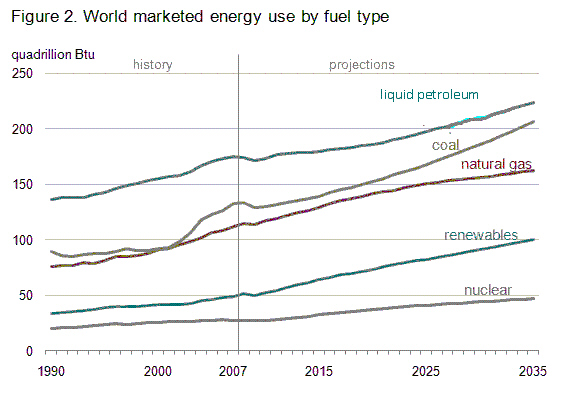 [Source: http://www.eia.doe.gov/oiaf/ieo/highlights.html]
|
|
|
55.
|
Use Figure 12-1. Which of the following statements is reasonable, according to
the information in the chart?
a. | Nuclear power will provide more energy than renewables by 2050. | b. | By 2050, fossil
fuels will no longer provide the majority of the world’s energy. | c. | In 2000, natural gas
provided about as much energy as coal. | d. | Renewables will be the largest source of energy
in the near future. | e. | The use of nuclear energy is decreasing over
time. |
|
|
|
Figure 12-3
 [Source:
http://www.eia.doe.gov/oiaf/1605/ggccebro/chapter1.html]
|
|
|
56.
|
Use Figure 12-3. Which of the following fuel types produces the highest ratio of
percent resulting CO2 emissions to percent consumption?
a. | Natural gas | b. | Non-fossil | c. | Coal | d. | Petroleum | e. | The ratios are the
same for all fuel types. |
|
|
|
Figure 12-4
|
|
|
57.
|
Use Figure 12-4. Based on the curve, it is believed that finding new petroleum
reserves
a. | will greatly increase the amount of time it will take to use up all available
reserves | b. | will greatly decrease the amount of time it will take to use up all available
reserves | c. | will slightly increase the amount of time it will take to use up all available
reserves | d. | will slightly decrease the amount of time it will take to use up all available
reserves | e. | will have no effect on the amount of time it will take to use up all available
reserves |
|
|
|
58.
|
In the use of coal to produce energy, which of the following does NOT decrease
the energy efficiency of the process?
a. | extracting the coal from the ground | b. | waste heat | c. | cogeneration | d. | energy required to build the power
plant | e. | the removal of the waste products |
|
|
|
59.
|
The energy source that can provide the greatest amount of electricity generation
in the United States due to its abundance is
a. | oil | b. | coal | c. | nuclear | d. | hydroelectric | e. | natural
gas |
|
|
|
60.
|
Environmental costs associated with the use of coal include all of the following
except
a. | particulates that are released into the atmosphere when coal is
burned | b. | degradation to land due to mining techniques | c. | the creation of
highly radioactive waste | d. | trace metals found in coal | e. | the transportation
of coal from mine to power plant |
|
|
|
61.
|
If an average refrigerator uses 500 watts of energy per hour on a daily basis,
and your energy cost is $0.11 per kwh, approximately how much does the energy used by the
refrigerator cost per month?
a. | $1.30 | b. | $13 | c. | $40 | d. | $55 | e. | $132 |
|
|
|
62.
|
Uranium-235 is considered ideal for nuclear reactors due to
a. | its wide distribution as a resource | b. | its stable nature as an
isotope | c. | its high EROEI | d. | its minimal production of radioactive
waste | e. | its fissionability |
|
|
|
63.
|
Which of the following is the correct type of energy utilized to produce tidal
power?
a. | Radiation | b. | Kinetic energy | c. | Solar
energy | d. | Potential energy | e. | Heat energy |
|
|
|
Table 13-1
| Type of Television | On Mode Power
Rating | | 50” Plasma
Television | 400 watts | | 52” LCD
Television | 220 watts | | 52” LCD Energy
Star Television | 120 watts | | |
|
|
|
64.
|
Use Table 13-1. If a community has 200,000 homes and 1% of those homes have
Plasma televisions, how many kWh of excess energy are being consumed every year (365 days) than if
those homes had Energy Star LCD televisions instead?
a. | 350,000 kWh | b. | 524,000 kWh | c. | 818,000
kWh | d. | 1,168,000 kWh | e. | 4.906,000 kWh |
|
|
|
Figure 13-1
|
|
|
65.
|
Use Figure 13-1. By looking at the chart above, what is the approximate percent
of the US energy needs are served by biomass energy sources?
a. | 1% | b. | 3.5% | c. | 10% | d. | 25% | e. | 56% |
|
|
|
Figure 13-2
Where Does My Money Go?
The annual energy bill
for a typical single home is approximately $2,200.
|
|
|
66.
|
Use Figure 13-2. Which of the following increases in efficiency would save a
typical household the most money?
a. | Increase heating efficiency by 5%. | b. | Use 25% less energy for
lighting. | c. | Increase cooling efficiency by 12%. | d. | Acquire appliances that are 15% more
efficient. | e. | Reduce electronics usage by 50% |
|
|
|
Figure 13-4
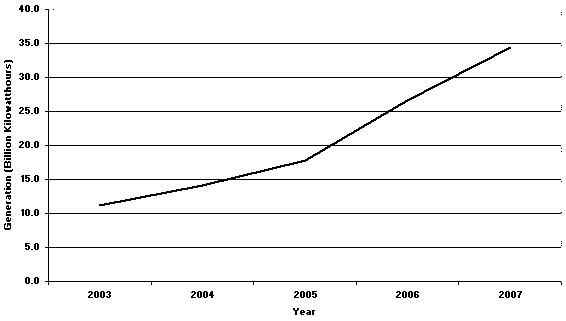
|
|
|
67.
|
Use Figure 13-4. If the trend from 2006 to 2007 continued, approximately how
many kWh would have been generated in 2008?
a. | 36 x 106 | b. | 36 x 109 | c. | 42 x
106 | d. | 42 x 109 | e. | 68 x
109 |
|
|
|
68.
|
Put the items below in correct sequence for the generation of electricity using
the wind
1 – generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy
2 – wind
turns the wind turbine blade
3 – the gear box transfers mechanical energy to the
generator
4 – electricity is transferred to the grid
a. | 1-2-3-4 | b. | 2-1-3-4 | c. | 2-3-1-4 | d. | 2-4-3-1 | e. | 4-2-3-1 |
|
|
|
69.
|
Which country is known for having the most available geothermal energy in the
world?
a. | Russia | b. | Iceland | c. | England | d. | China | e. | France |
|
|
|
70.
|
Which form of energy production has a large environmental impact, a high cost of
construction, and the potential to force the displacement of large numbers of people and
wildlife?
a. | water impoundment systems | b. | photovoltaic systems | c. | wind
farms | d. | tidal power generating stations | e. | geothermal power
stations |
|
|
|
71.
|
The BOD measurement of a liter of healthy water was found to be 20 mg. The BOD
measurement of a liter of more polluted water was 120 mg. Which of the following statements is
correct?
a. | the healthy water produced 6 times as much oxygen as the polluted
water. | b. | the polluted water produced 6 times as much oxygen as the healthy
water. | c. | the healthy water consumed 6 times as much oxygen as the polluted
water. | d. | the polluted water consumed 6 times as much oxygen as the healthy
water. | e. | None of these answers are correct. |
|
|
|
72.
|
Concerns over the wide use of synthetic pesticides include all of the following
unintended effects EXCEPT
a. | the pesticide may be lethal to nontarget species as well as target
species | b. | pesticide use leads to an altered species composition of the
community | c. | the chemistry of the inert ingredients | d. | physiological side effects on pest and nonpest
species | e. | acidification of nearby streams |
|
|
|
73.
|
Possible sources of petroleum in the ocean waters include all of the following
EXCEPT
a. | naturally occurring plumes from oceanic trenches | b. | natural seeps from
the ocean floor | c. | oil tanker transportation | d. | oil platform leaks | e. | tanker or platform
accidents |
|
|
|
74.
|
The material rotating in the North Pacific Gyre can best be described as
a. | solid waste composed of mostly plastics | b. | organic waste dumped
from cruiseships | c. | medical waste dumped by the United States | d. | coal slag dumped by
China | e. | solid waste from countries without landfills |
|
|
|
75.
|
Ground level ozone is classified as a pollutant because it reduces lung
functionality AND
a. | its concentrations are low but the particle size is high | b. | it occurs in the
atmosphere only | c. | it is entirely anthropogenic in nature | d. | it can degrade plant
surfaces | e. | it is an unstable molecule |
|
|
|
76.
|
Which of the following correctly lists the 6 “criteria” air
pollutants as specified under the Clean Air Act?
a. | Pb, SO2, NOX, CO, PM, and tropospheric
O3 | b. | Tropospheric O3, SO2, NOX, PM, Pb, and
CO2 | c. | SO2, NOX, Hg, Pb, PM, and O3 | d. | SO4,
NOX, CO, PM, Pb, and tropospheric O3 | e. | SO2,
NOX, CO, Hg, PM, and tropospheric O3 |
|
|
|
77.
|
The movement of large polluted air masses across the Pacific ocean into the
northern United States is an example of
a. | the effects of the impact of the low air quality standards of ocean transport
vehicles | b. | a violation of the Montreal Protocol | c. | the ill effects of increased UV
radiation | d. | a violation of the Clean Air Act | e. | a reason that collaborative international air
quality legislation would be useful |
|
|
|
78.
|
The air pollutant that is a metal and is released primarily from the combustion
of coal is
a. | lead | b. | mercury | c. | arsenic | d. | sulfur | e. | none of the
above |
|
|
|
79.
|
A thermal inversion, which can lead to serious pollution events, occurs
when
a. | warm air that normally rises, does so taking the pollutants with
it | b. | warm air that normally rises stays close to the surface holding pollutants close to
the surface | c. | cool air that normally rises, does so taking the pollutants with
it | d. | cool air stays close to the surface but pollutants rise into the
atmosphere | e. | cool air stays close to the surface and is blanketed by a layer of warm air that
traps pollutants |
|
|
|
80.
|
The correct sequence of events for acid deposition are
W. deposition of ions
on vegetation or soil
X. secondary pollutants are formed
Y. combustion releasing SO2
and NOX
Z. dissociation of pollutants
a. | Z->X->Y->W | b. | Y->X->Z->W | c. | Y->Z->X->W | d. | Y->W->X->Z | e. | Z->Y->W->X |
|
|
|
81.
|
Which of the following is NOT a problem associated with acid deposition?
a. | compromised aquatic systems | b. | lowered pH of lakes | c. | negative effects on
human skin with contact | d. | erosion of buildings and monuments made of
marble | e. | erosion of paint on painted surfaces |
|
|
|
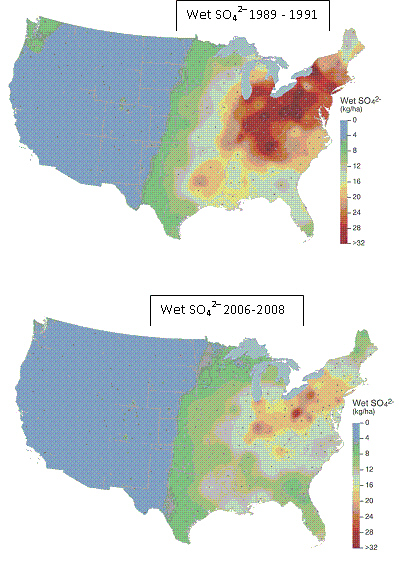
Figure 15-3
|
|
|
82.
|
Use Figure 15-3. The change in acid deposition for the southern half of the
state of Michigan from 1989-1991 to 2006-2008 is
a. | a decrease of approximately 5% | b. | a decrease of approximately
50% | c. | it has stayed relatively the same | d. | an increase of approximately
1% | e. | an increase of approximately 5% |
|
|
|
83.
|
The depletion of ozone over Antarctica is greatest during
a. | August through November | b. | December through February | c. | February through
May | d. | June through August | e. | the ozone hole is consistent in size throughout
the year |
|
|
|
Figure 15-5
Number of people living in countries with air
quality concentrations above the level of the primary national Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS)
in 2006.
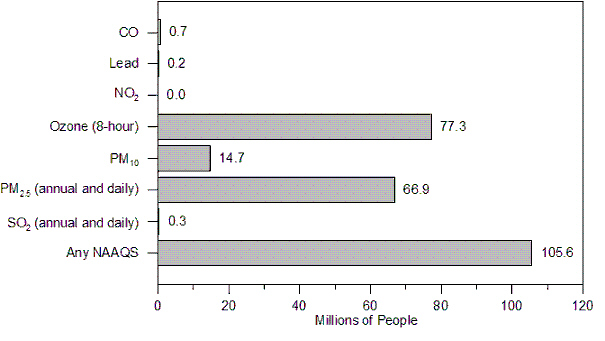
|
|
|
84.
|
Use Figure 15-5. In 2006, the total population of the U.S. was approximately
300,000,000 people. About what percent of those people lived in counties where carbon monoxide levels
exceeded the NAAQS?
a. | 0.2% | b. | 0.7% | c. | 2% | d. | 20% | e. | 70% |
|
|
|
85.
|
Which harmful substance was once commonly used as insulation?
a. | asbestos | b. | mercury | c. | lead | d. | radon | e. | ozone |
|
|
|
86.
|
In the waste stream, the most optimal way to achieve a reduction in MSW
production is
a. | recycle metal components | b. | reduce input by waste
prevention | c. | purchase recycled materials | d. | compost organic waste | e. | reuse water in a
closed-loop system |
|
|
|
87.
|
Which of the following is/are environmental benefit/s of recycling
aluminum?
I. Reduces the effects on the land from mining
II. Reduces the effects of leaching in
landfills
III. Reduces the energy required to transport and process mined ore
a. | I only | b. | II only | c. | I and II
only | d. | I and III only | e. | I, II, and III |
|
|
|
88.
|
Which of the following is least likely to be a danger associated with leachate
from a sanitary landfill?
a. | The leachate can leak into nearby soils | b. | The leachate can
leak into groundwater | c. | The leachate can contain toxic metal
compounds | d. | The leachate can be at a high temperature | e. | The leachate can be
classified as toxic waste and have to be treated accordingly |
|
|
|
89.
|
A landfill in Minnesota receives an average of 50 cm of rainfall per year. 60
percent of the water runs off the landfill. The landfill has a surface area of 5000 m2.
The leachate from the landfill is treated for cadmium and other toxic metals. The present leachate
collection system is 80% efficient. What is the volume of leachate that is treated per year?
a. | 1600 m3 | b. | 1000 m3 | c. | 960
m3 | d. | 800 m3 | e. | 200
m3 |
|
|
|
90.
|
The US legislation that imposes a tax on targeted industrial facilities and then
utilizes those funds to cleanup selected abandoned hazardous waste sites is
a. | NEPA | b. | CWA | c. | CERCLA | d. | RCRA | e. | NPA |
|
|
|
91.
|
A historical pandemic disease caused by a bacterium and carried by rodents
is
a. | Cholera | b. | Tuberculosis | c. | Plague | d. | Swine Flu | e. | Hepatitis |
|
|
|
92.
|
Studies that last for only 1 to 4 days in which scientists measure mortality of
organisms as a response to a dose of a chemical are known as
a. | acute studies | b. | biomagnification studies | c. | prospective
studies | d. | chronic studies | e. | retrospective
studies |
|
|
|
93.
|
Which of the following factors are important in promoting species endangerment
and ultimately extinction?
I. habitat destruction
II. exotic species introduction
III.
increased tropospheric ozone
a. | I | b. | I and III | c. | I and
II | d. | III | e. | I, II, and III |
|
|
|
94.
|
Which of the following poses the greatest obstacle to the protection of
threatened or endangered species?
I. too much regulation makes action slow
II. lack of
international treaties to protect species
III. enforcement of laws is lacking because of poor
funding or support
a. | I and II | b. | II | c. | I, II, and
III | d. | I and III | e. | III |
|
|
|
95.
|
Which of the following energy sources is a chief contributor to greenhouse gas
emissions as well as increasing environmental mobility of mercury?
a. | Nuclear Power | b. | Wind Power | c. | Coal | d. | Natural gas cogeneration | e. | Hydropower |
|
|
|
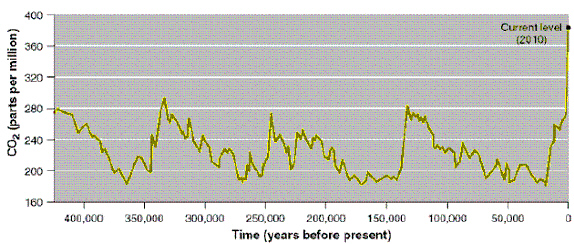
Figure 19-2
|
|
|
96.
|
Use Figure 19-2. Between 400,000 and 10,000 years ago, the highest
CO2 concentration was approximately
a. | 380 ppm | b. | 320 ppm | c. | 290
ppm | d. | 200 ppm | e. | 180 ppm |
|
|
|
Table 19-1
Greenhouse gas emission by livestock category in
2005
| Animal
Type | Total CO2 emission equivalent (millions of
metric tons) | | Beef cattle | 168.3 | | Dairy cattle | 51.2 | | Swine | 21.0 | | Poultry | 3.1 | | |
|
|
|
97.
|
Use Table 19-1. In 2005, there were approximately 60.6 million swine in the U.S.
About how much emissions did EACH of these swine produce?
a. | 0.035 metric tons | b. | 0.35 metric tons | c. | 3.5 metric
tons | d. | 35 metric tons | e. | 3500 metric
tons |
|
|
|
Figure 19-3
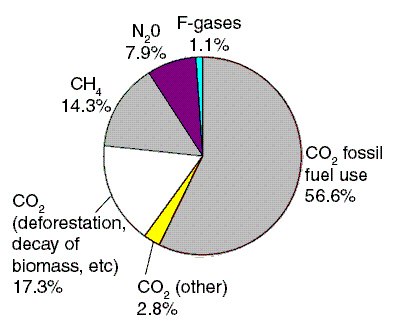
|
|
|
98.
|
Use Figure 19-3. Ignoring CO2 emissions caused by fossil fuel use,
which would be the best practice to reduce anthropogenic greenhouse gases?
a. | eliminate the use of ozone-depleting chemicals | b. | convert wetlands
into agricultural land | c. | institute policies that reduce deforestation
worldwide | d. | increase the use of nitrogen based fertilizer | e. | subsidize logging in
the pacific northwest |
|
|
|
99.
|
The concentration of which of the following greenhouse gases is LEAST affected
by human activity?
a. | water vapor | b. | carbon dioxide | c. | chlorofluorocarbons | d. | methane | e. | carbon
monoxide |
|
|
|
100.
|
Approximately three billion people live on less than two U.S. dollars per
day. This level of poverty has a resounding impact on the environment in the form of:
a. | heavy metal refining | b. | increased production of
plastic | c. | reduction in water quality from lack of sanitation facilities | d. | reforestation of
agricultural fields | e. | reduction in human population from inability to
afford children |
|
Essay
|
|
|
1.
|
Free Response Questions #1
You have been
put in charge of a new national park. Your goal is to help restore the biodiversity of the area
while at the same time allowing visitors to the park.
A.
Describe TWO ways you could measure the health of the
ecosystem. (2 points, one for each answer)
B.
Would you describe the national park as an open or a closed system and how would
this help you in your management? (2 points, one for identifying an open system and one for
how this would help in your management)
C.
There are many valuable services that ecosystems
provide. List TWO ecosystem services that your park could provide and explain each. (2
points, one for each service with a complete description.)
D. Knowing the type of biome your park is in will help you in both your
conservation efforts as well as how and when people should come to the park. As you survey the
park you find it has over 1 m of precipitation annually. The park has warm summers and cold
winters. The park is dominated by broadleaf deciduous trees such as beech, maple, oak and
hickory. Identify what biome your park is in, and how the knowledge affects how you plan to
manage the park. (2 points, one for identifying that the park is in the temperate seasonal
forest biome and one for describing how the biome might affect the management of the
park).
E. As
you walk through the park you discover that one area has been altered due to human logging.
This area contains large numbers of two species of trees that are valuable to the lumber industry,
but has few other species of trees. The rest of the park consists of hundreds of different
species of trees scattered randomly about. What specific measurements could you use to compare
the biodiversity of the two areas? How does knowing this information help you in deciding how to
manage the logged area? (2 points, one for how to evaluate the biodiversity and one for how
this information will help you.)
|
|
|
2.
|
Free Response Question #2
With an
ever-increasing human population, people are moving to cities at a growing rate. This creates
both social and environmental impacts.
a. The world’s growth rate was 1.14% in
2010. At this growth rate, about how many years will it take for the world population to
double? (1 point)
b. Identify TWO ways the move to cities
will affect the soil in the area. (2 points)
c. Describe TWO ways
the enlarging city could affect the biodiversity. (2
points)
d. Identify ONE human health issue that can result when
people are living in a densely populated area. (1 point)
e. Describe how
wilderness areas are affected by urban sprawl as people move to cities. Describe TWO ways this
impact could be reduced. (4 points; 2 points for the description of how wilderness areas
are affected and 2 points for the two ways this could be reduced)
|
|
|
3.
|
Free Response Question #3
The city of
Freemont has outgrown its current coal burning power plant. The city council is considering
many options, including different renewable energy sources, as well as rebuilding the existing power
plant to accommodate the growing city.
a) Identify
TWO renewable energy sources the town could consider and describe a benefit and a cost of each.
(6 pts; 2 pts for the two energy sources and a point for each benefit and cost)
b) The
current power plant has a capacity of 1000 MW and a capacity factor of 0.9. In Freemont, the average
home uses approximately 1000 kWh of electricity per month. How many homes can the current power plant
provide electricity for? (2 points; 1 for set up and 1 for correct
answer)
c) Many
residents of Freemont have been experiencing lung and respiratory
illnesses. It is discovered that the power plant is polluting a common
that the residents all share, the air. Name a common other than the air and describe an
economic solution for better managing this common. (2 points; 1 pt for the common and 1 pt for
the solution)
d) Name ONE strategy the government
could enact to protect the common. (1 point)
|
|
|
4.
|
Free Response Question #4
The city of Lakeville has a landfill on the south side of the city. This
landfill has been open for 20 years and is nearly full. The town is considering installing
methane collectors in the landfill to use for energy. This will help lessen the demand on the
existing coal-burning power plant, which currently supplies the town with all of its energy.
a. The town has 1000 homes, with the average home having 4 people. The average energy
use per person is 2500 kWh per year. Calculate the yearly demand on the power plant for
electrical energy. (2 pts, 1 for set up and 1 for correct answer)
b. Give TWO practical
strategies that members of the community could do to reduce their overall energy consumption. (2 pts,
1 for each strategy)
c. List and describe TWO environmental benefits and TWO
environmental costs of using methane to make energy. (4 pts, 1 pt
for each benefit and 1 pt for each cost)
d. Name ONE human health concern that is
associated with landfills and suggest a solution to this problem. (2 pts, 1 pt for the human health
concern and 1 pt for a solution)
|